[Next] [Previous] [Up] [Top] [Contents] [Index]
13. Expressions
13. 2. Values
Depending on the context, an expression can use values of a data item. If an expression is evaluated for a data item, it can use the values of this item. E. g. an expression that is an argument of a command that operates on atoms can use the values of this atom, like its name. The following is a table of the values that are valid for each data item:
item | value | type | explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| | integer | molecule number |
| | integer | molecule number |
| | integer | residue number |
| | integer | residue number |
| | integer | primary number |
| | integer | primary number |
| | string | molecule name |
| | string | residue name |
| | string | atom name |
| | string | angle name |
| | float | chemical shift of atom |
| | float | B factor of atom |
| | float | van der Waals radius of atom |
| | float | partial charge of atom |
| | float | charges on heavy atoms |
| | float | averaged charges on heavy atoms |
| | float | simple charges from setup file |
| | float | distance from reference atom(s) |
| | float | angle |
| | float | distance |
| | float | limit of constraint |
| | float | violation of constraint |
| | bool | true if distance is upper limit |
| | bool | true if distance is lower limit |
| | bool | true if distance is H-bond |
| | integer | graphics attribute index |
| | integer | graphics attribute index |
| | integer | graphics attribute index |
| | integer | graphics attribute index |
Values of an item can be referenced by just using their name. It is also possible to access values of items that are higher in the data hierarchy. This is done in the form item.value, e. g. res.name in an expression that is evaluated for an atom. The following figure shows the data hierarchy:
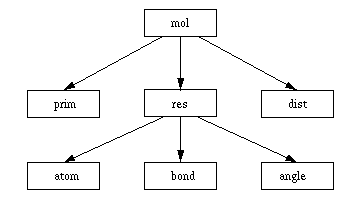
Not all primitives belong to a molecule. For the ones that do not (titles), accessing molecule values will result in null values (0 for the number, empty string for the name).
For bonds, distances and angles, it is also possible to access the values of the atoms involved. For bonds this is done by using the items atom1 and atom2, for dihedral angles the 4 atoms defining it can be accessed over atom1, atom2, atom3, and atom4.
For bonds and distances, it is also possible to access the values of both residues involved. This is done by using the items res1 and res2.
For distances, it is also possible to access the values of both molecules involved. This is done by using the items mol1 and mol2.
Examples
nameres.numatom1.name